When we talk about cybersecurity events, we often discuss “the three principles of security” — which can be abbreviated as “CIA”:
- The confidentiality of the information: Confidentiality is what comes to mind most frequently when we consider cybersecurity breaches. If an attacker is able to access personal information and use it for nefarious purposes, confidentiality has been broken.
- The integrity of the information: Integrity refers to information in its original format that hasn’t been manipulated by a bad actor.
- The availability of the information: Availability can be impacted by distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, which we’ll discuss below. If an attacker is able to bring down a service for a period of time, people may not be able to access the information they want or need.
Now, more than ever, bad actors leverage a variety of attack vectors to infiltrate a network or disrupt access to sensitive data — thereby compromising the three principles outlined above.
3 Common attack vectors (and how to avoid them)
In today’s ever-evolving cybersecurity environment, many types of breaches and other security incidents are caused by one of the following attack vectors:
Phishing attack
To conduct a phishing attack, a bad actor tries to impersonate either a legitimate person or a corporation (for example, a company that the person they’re phishing does business with) through an email that asks the user to take an action that would give the phisher an access point to critical data or information.
Bad actors using phishing attacks often try to spoof the logo or website of a well-known corporation or individual so their email request appears legitimate. For instance, a hacker may try to get someone in the finance department of a company to transfer funds to the hacker’s account by spoofing an email to look like the recipient's bank. We’ve also seen phishers try to obtain employee information — like W-2 records. They do this by posing as a trusted source and reaching out to someone in the HR department to see if they’ll send the information.
To avoid a phishing attack, it’s critical to teach employees to pay close attention to anything that may be slightly wrong with an email, including misspellings, strange syntax, or logos that have been slightly altered. You should also teach employees never to click on a link within an email. For example, if an employee is contacted by their bank and encouraged to reset a password, it’s best to go directly to the bank’s website.
SQL injection attack
Structured query language (SQL) is a programming language used to deal with back-end databases and applications. SQL injection attacks have been around for a long time, but are still commonly used to exploit companies. If a web developer creates an application where the user can interact with a database to add information — and this developer does not take proper precautions — an attacker can perform a “get request” or “select request” function, which essentially dumps the entire database so they can harvest sensitive information.
To avoid a SQL injection attack, be sure to have these precautions in place:
- Create validation standards for the information you’re allowing to come into your database. This includes adding character limits for usernames and passwords.
- Outlaw certain characters that are associated with SQL injection requests. This makes it more difficult (or even impossible) for an attacker to send information to your database and have it enumerate anything.
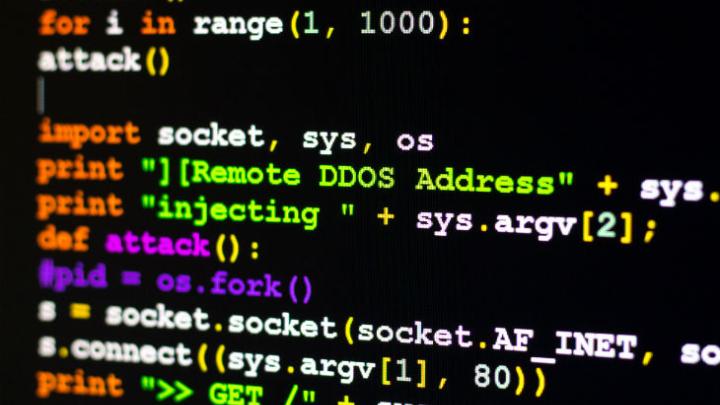
DDoS attack
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks impact information availability. This attack vector comes into play when a bad actor creates a slew of traffic requests on a website at once in order to crash it or severely cripple it for a period of time.
Many websites are not set up to handle the kind of traffic that attackers can harness using botnets — making them increasingly susceptible to this particular attack vector. Interestingly, much of the news coverage that tends to surround DDoS attacks is political. “Hacktivist” groups are known to perform DDoS attacks on government and corporate websites for political purposes. DDoS attacks happen all the time to many other types of organizations as well — but those that get the most news coverage are able to bring down a website or cause a noticeable disruption in service.
To avoid a DDoS attack, employ DDoS prevention services. These are often provided by hosting companies who are able to help your website handle large influxes of traffic in case of a DDoS event.
Tackling cyber risk throughout your organization
When you’re dealing with attack vectors that lead to different types of cybersecurity breaches, employee vigilance and attention to detail are very important. It’s critical to train all employees on the common methods used to compromise valuable data — and how to avoid them. For instance, you can help to protect your organization from experiencing the damaging reputational and financial impacts of a breach by conducting thorough employee training on topics such as how to avoid clicking links that could lead to a phishing attack.
Of course, with the widespread shift to remote work, this type of education is more important than ever before. In order to monitor and manage the inherent risk present throughout your expanding attack surface, you need to update employee trainings based on our “new normal” environment, gain visibility into all of your critical assets, and have a robust security performance management program in place.
This post was updated in August 2020 to include new Bitsight and industry information.