
Supply chain cybersecurity and resilience have become pivotal across various cyber regulations, most notably NIS2 and DORA. In this blog, stemming from our latest ebook '5 Proven Strategies to Maximize Supply Chain Cyber Risk Management’, we will explore the reasons why resilience is a new mandate for CISOs today and, most importantly, how to secure the supply chain at scale—in line with evolving regulatory requirements.
The Imperative of Supply Chain Risk Management
Regulations aren't arbitrary mandates—they are responses to the increasing recognition of supply chain attacks as significant threats to national and economic security, with implications on the continuity of critical services and infrastructure.
The push for compliance is complemented by the business imperative of trust. In the digital economy, customer trust is paramount, and a single breach through a supply chain partner can erode years of goodwill. Cybersecurity leaders are not just managing risk—they're being called to set new benchmarks for trust and resilience.
Furthermore, the advent of technologies such as AI and the increasing reliance on cloud services have expanded the attack surface exponentially. Each new technology adopted by a supplier becomes a new frontier for cyber threats. Without a comprehensive strategy for supply chain cybersecurity, these technologies can turn from tools to liabilities overnight.
Not to mention the economic argument for prioritizing supply chain cybersecurity. The costs associated with cyber incidents —from operational disruption to legal penalties and beyond— can be devastating. By investing in supply chain cybersecurity, organizations are not just preventing potential breaches; they're also avoiding the significant financial repercussions that can follow.
The following reasons summarize the importance of a comprehensive approach to supply chain cybersecurity and resilience, as reflected in the increasing focus of cyber regulations globally:
- Global Interconnectivity and Dependency: The intricate web of global supply chains means a vulnerability in one link can have cascading effects across borders and industries, like MOVEit proved. Regulations emphasize supply chain security to mitigate these risks.
- Rise in Sophisticated Cyber Attacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting supply chains as entry points to larger ecosystems. Regulations aim to raise the bar for cybersecurity practices across all entities within the supply chain, not just the end targets, to counteract these evolving threats.
- Economic and National Security: Supply chain disruptions can have significant economic repercussions and pose risks to national security, especially when critical infrastructure or essential services are affected. Cyber regulations thus prioritize supply chain resilience to protect economies and national security interests from cyber threats.
- Consumer Protection and Trust: Consumers are increasingly concerned about the security of their data and the integrity of the products and services they use. Regulations that focus on supply chain cybersecurity work towards ensuring that consumer data is protected at every stage, building trust in digital services and products.
- Adaptation to Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological change, including the adoption of cloud services, IoT devices, and AI, expands the attack surface and introduces new vulnerabilities. Regulations are evolving to address these changes, ensuring that supply chain cybersecurity measures are robust, adaptive, and capable of safeguarding against both current and future cyber threats.
Cyber Leadership in Action: Spearheading Supply Chain Resilience to Meet Regulatory Demands
Cyber risk management strategies demand not just oversight but foresight. So how can cybersecurity leaders be more resourceful as they look to maintain a best-in-class program and continue to meet business —and regulatory— expectations?
In our latest ebook, '5 Proven Strategies to Maximize Supply Chain Cyber Risk Management’, you'll find the real talk on how to scale up your third-party risk management without just throwing more people at the problem. You’ll learn how to get smarter with the resources you’ve got, making sure you can spot the red flags before they become headlines.
From laying the foundations of a robust vendor risk assessment framework to adopting an eagle-eyed stance for continuous monitoring and crafting a collaboration-first approach to accelerate vulnerability remediation—this guide is your map to maximize supply chain cybersecurity amid new regulations by means of an integrated Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) program.
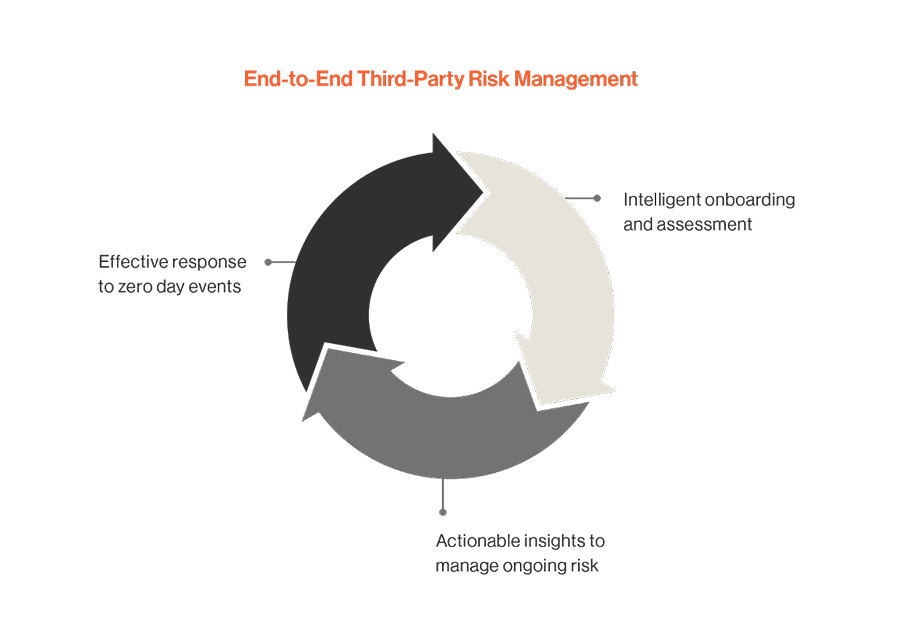
Complexity may be a given, but simplicity is our choice. By embracing the simplicity of a streamlined, integrated strategy, cybersecurity leaders can focus on what they do best: protecting their organizations in an increasingly interconnected and fast-paced world.
This isn’t about ticking boxes. It’s about giving you the tools to build something solid—so that when you’re in the hot seat, you can say with confidence, “We’ve got this.”